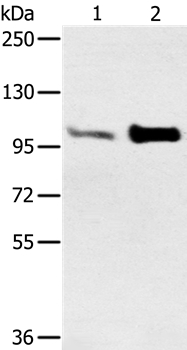
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103219/GTX103219_44335_20210702_WB_M_22072519_433.webp)
Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3]
GTX103219
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Porcine, Rat, Zebra Fish
TargetACTN2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Namealpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:10000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.18 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID88
- Target nameACTN2
- Target descriptionactinin alpha 2
- Target synonymsCMD1AA, CMH23, CMYO8, CMYP8, MPD6, MYOCOZ, alpha-actinin-2, F-actin cross-linking protein, alpha-actinin skeletal muscle
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP35609
- Protein NameAlpha-actinin-2
- Scientific DescriptionAlpha actinins belong to the spectrin gene superfamily which represents a diverse group of cytoskeletal proteins, including the alpha and beta spectrins and dystrophins. Alpha actinin is an actin-binding protein with multiple roles in different cell types. In nonmuscle cells, the cytoskeletal isoform is found along microfilament bundles and adherens-type junctions, where it is involved in binding actin to the membrane. In contrast, skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle isoforms are localized to the Z-disc and analogous dense bodies, where they help anchor the myofibrillar actin filaments. This gene encodes a muscle-specific, alpha actinin isoform that is expressed in both skeletal and cardiac muscles. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Porcine, Rat, Zebra Fish
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![Rat tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:20000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Rat tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:20000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103219/GTX103219_44335_20210709_WB_R_heart_22072519_163.webp)
![alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] detects alpha Actinin 2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse heart. alpha Actinin 2 stained by alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] detects alpha Actinin 2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse heart. alpha Actinin 2 stained by alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103219/GTX103219_44566_20220729_IHC-P_M_1_22080119_266.webp)
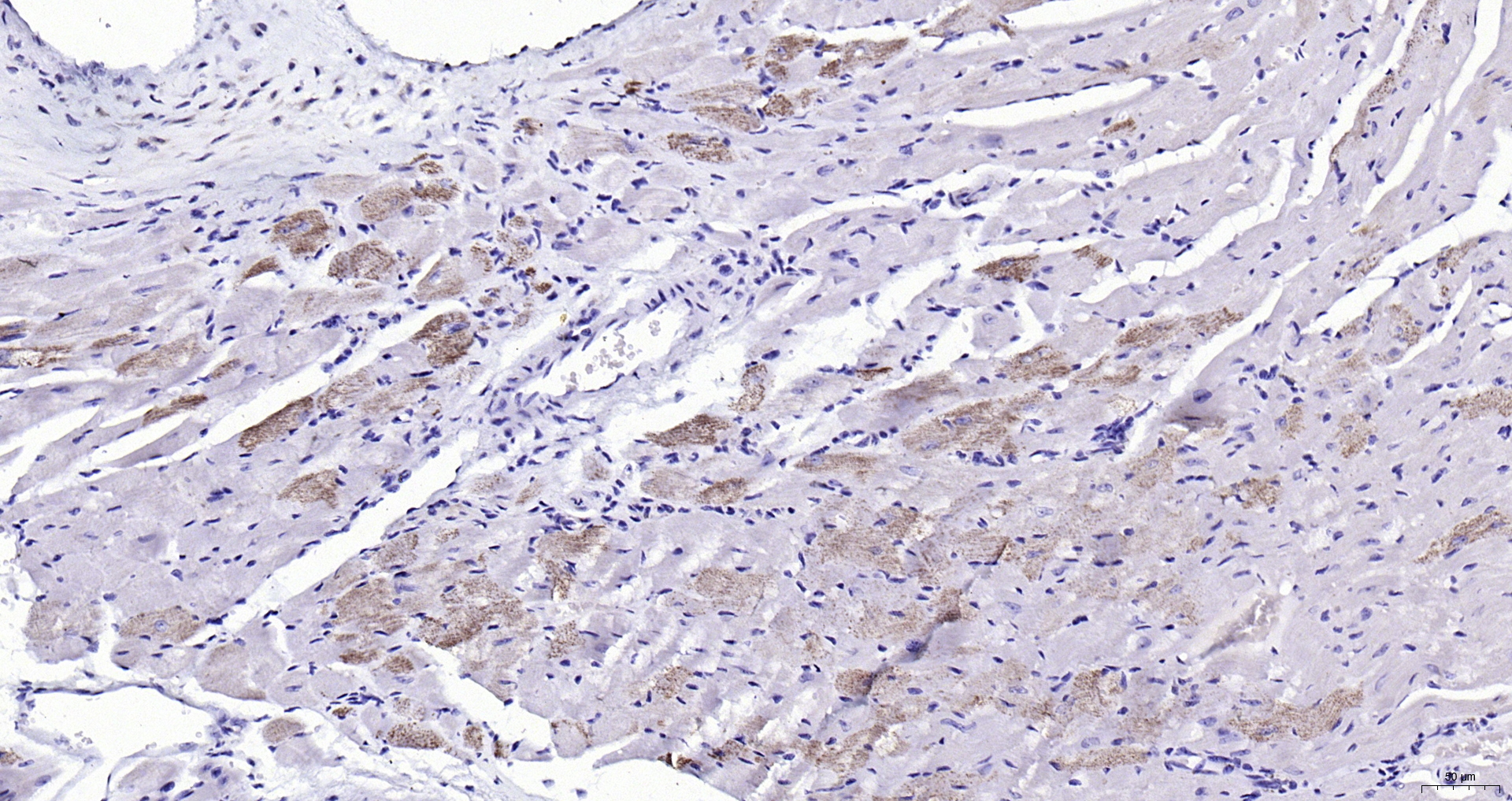
![alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] detects alpha Actinin 2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat heart. alpha Actinin 2 stained by alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] detects alpha Actinin 2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat heart. alpha Actinin 2 stained by alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103219/GTX103219_44567_20220729_IHC-P_R_22080119_592.webp)
![alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] detects alpha Actinin 2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse muscle. alpha Actinin 2 stained by alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] detects alpha Actinin 2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse muscle. alpha Actinin 2 stained by alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103219/GTX103219_44566_20220729_IHC-P_M_22080119_662.webp)
![Whole zebrafish extract (30 μg) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Whole zebrafish extract (30 μg) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103219/GTX103219_44335_20210917_WB_Z_22111423_383.webp)
![Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:100000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:100000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103219/GTX103219_44524_20211217_WB_M_heart_23041723_474.webp)
![alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] detects alpha Actinin 2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse muscle. alpha Actinin 2 stained by alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] detects alpha Actinin 2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse muscle. alpha Actinin 2 stained by alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103219/GTX103219_44524_20220114_IHC-P_M_1_23041723_970.webp)
![alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] detects alpha Actinin 2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse heart. alpha Actinin 2 stained by alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] detects alpha Actinin 2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse heart. alpha Actinin 2 stained by alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103219/GTX103219_44524_20220114_IHC-P_M_23041723_798.webp)
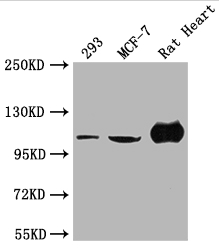
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N1N3] (GTX103219) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103219/GTX103219_44524_20211217_WB_23050223_219.webp)




![Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with alpha Actinin 2 antibody [N2C1], Internal (GTX111167) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX111167/GTX111167_40086_20220812_WB_M_tissue_22081423_498.webp)