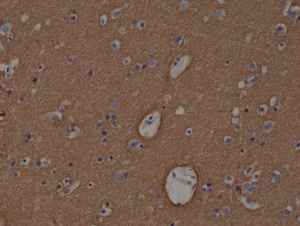
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human brain tissue section using anti-Syntaxin-1A rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM367) at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-Syntaxin-1A (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM367)
REV-31-1253-00
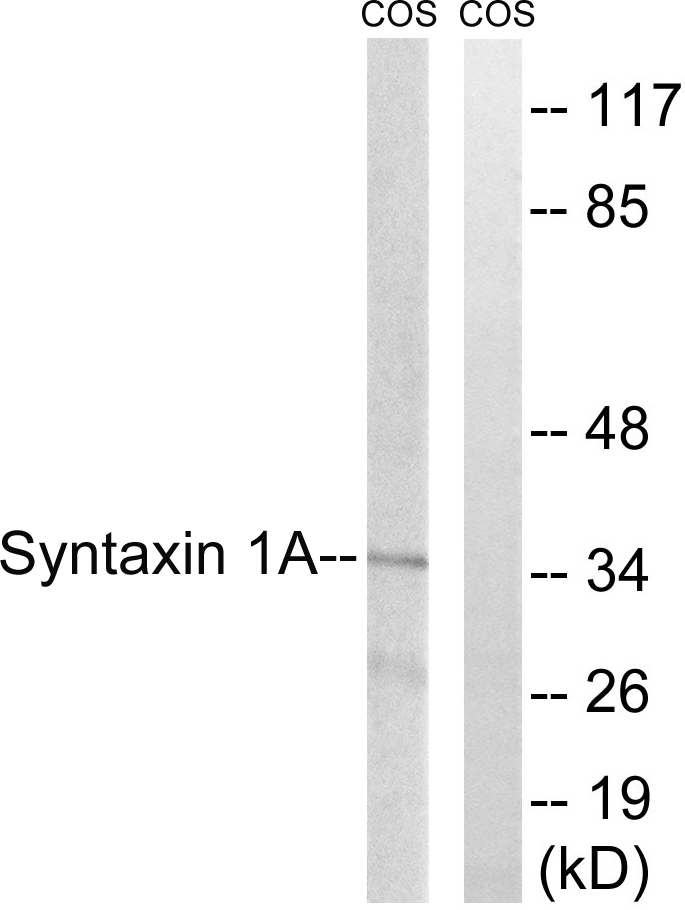
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSTX1A
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Syntaxin-1A (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM367)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM367
- Gene ID6804
- Target nameSTX1A
- Target descriptionsyntaxin 1A
- Target synonymsHPC-1, P35-1, STX1, SYN1A, syntaxin-1A, neuron-specific antigen HPC-1, syntaxin 1A (brain)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ16623
- Protein NameSyntaxin-1A
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human, mouse, and rat Syntaxin-1A. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Synaptic vesicles store neurotransmitters that are released during calcium-regulated exocytosis. The specificity of neurotransmitter release requires the localization of both synaptic vesicles and calcium channels to the presynaptic active zone. Syntaxins function in this vesicle fusion process. Syntaxin-1A (Neuron-specific antigen HPC-1) belongs to the Q-SNARE protein family that participates in exocytosis. Syntaxin-1A is a t-SNARE abundantly expressed in most neurons and localized on the neuronal plasma membrane, where it participates in the formation of the trans-SNARE complex by engaging t-SNARE SNAP25 (synaptosomal-associated protein 25) and v-SNARE synaptobrevin (a.k.a. vesicle-associated membrane protein2 or VAMP2) to allow fusion between the synaptic vesicle and plasma membrane. Two types of syntaxin 1 isoforms exist. Syntaxin-1A is a key protein in ion channel regulation and synaptic exocytosis. - Synaptic vesicles store neurotransmitters that are released during calcium-regulated exocytosis. The specificity of neurotransmitter release requires the localization of both synaptic vesicles and calcium channels to the presynaptic active zone. Syntaxins function in this vesicle fusion process. Syntaxin-1A (Neuron-specific antigen HPC-1) belongs to the Q-SNARE protein family that participates in exocytosis. Syntaxin-1A is a t-SNARE abundantly expressed in most neurons and localized on the neuronal plasma membrane, where it participates in the formation of the trans-SNARE complex by engaging t-SNARE SNAP25 (synaptosomal-associated protein 25) and v-SNARE synaptobrevin (a.k.a. vesicle-associated membrane protein2 or VAMP2) to allow fusion between the synaptic vesicle and plasma membrane. Two types of syntaxin 1 isoforms exist. Syntaxin-1A is a key protein in ion channel regulation and synaptic exocytosis.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161






![Syntaxin 1a antibody [N1], N-term detects Syntaxin 1a protein at cell body and synaptic vesicles by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV9 rat E18 primary cortical neurons were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Syntaxin 1a protein stained by Syntaxin 1a antibody [N1], N-term (GTX106365) diluted at 1:500. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1, a neuron cell marker, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 antibody [GT11710] (GTX631836) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX106365/GTX106365_39715_20170727_IFA_R_w_23060120_748.webp)