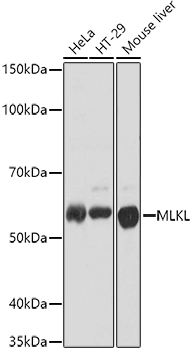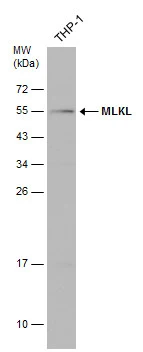
Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with MLKL antibody (GTX107538) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
MLKL antibody
GTX107538
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetMLKL
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameMLKL antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.52 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID197259
- Target nameMLKL
- Target descriptionmixed lineage kinase domain like pseudokinase
- Target synonymshMLKL, mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ8NB16
- Protein NameMixed lineage kinase domain-like protein
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161




![IHC-P analysis of human skin tissue using GTX34079 MLKL antibody [8H7]. Dilution : 1:200](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX34079/GTX34079_20200622_IHC-P_357_w_23060801_241.webp)


![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with MLKL antibody [HL1849] (GTX637574) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX637574/GTX637574_44872_20221125_WB_22112723_689.webp)